Logical Reasoning and Analytical Ability
1. How many meaningful English words can be formed with the letters AMRE using each letter only once in each word ?
(a) None
(b) One
(c) Two
(d) Three
(e) More than three
2. How many such digits are there in the number 42519673 each of which is as far away from the beginning in the number as when the digits are arranged in ascending order within the number ?
(a) None
(b) One
(c) Two
(d) Three
(e) More than three
3. In a certain code MODERN is written as 5% 38#@ and WIN is written as 6©@. How is RIDE written in that code ?
(a) #©38
(b) #@38
(c) #©83
(d) ©@38
(e) None of these
4. What should come next in the following number series ?
2 2 3 2 3 4 2 3 4 5 2 3 4 5 6 2 3 4 5 6 7 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
(a) 3
(b) 2
(c) 9
(d) 7
(e) None of these
5. Four of the following five are alike in a certain way and so form a group. Which is the one that does not belong to that group ?
(a) Sodium
(b) Chlorine
(c) Magnesium
(d) Nitrogen
(e) Glucose
6. How many such pairs of letters are there in the word BAROMETER each of which has as many letters between them in the word as in the English alphabet ?
(a) None
(b) One
(c) Two
(d) Three
(e) More than three
7. Four of the following five are alike in a certain way and so form a group. Which is the one that does not belong to that group ?
(a) Radish
(b) Carrot
(c) Garlic
(d) Gourd
(e) Ginger
8. Four of the following five are alike in a certain way and so form a group. Which is the one that does not belong to the group ?
(a) 39
(b) 69
(c) 57
(d) 129
(e) 117
9. In a certain code HEALING is written as BRFIKHOJ. How is BEDTIME written in that code ?
(a) EFCSJNF
(b) EFCSFNJ
(c) EFCUFNS
(d) CFESFNJ
(e) None of these
10. If it is possible to make only one meaningful English word with the second, the fifth, the seventh and the eleventh letters of the word STAKEHOLDER, which of the following will be the third letter of that word? If no such word can be made, give ‘X’ as the answer and if more than one such word can be formed, give ‘Y’ as the answer.
(a) T
(b) R
(c) E
(d) X
(e) Y
Directions (Q. 11-15) : Each of the questions below consists of a question and two statements numbered I and II are given below it. You have to decide whether the data provided in the statements are sufficient to answer the question. Read both the statements and
Give answer (a) : If the data in Statement I alone are sufficient to answer the question, while the data in Statement II alone are not sufficient to answer the question
Give answer (b) : If the data in Statement I alone or in Statement II alone are sufficient to answer the question.
Give answer (c) : If the data in Statement I alone or in Statement II alone are sufficient to answer the question
Give answer (d) : if the data in both the Statements I and II are not sufficient to answer the question
Give answer (e) : If the data in both the Statements I and II together are necessary to answer the question
11. What does ‘Pe’ mean in a code language ?
I. ‘Na Si La Lo’ means ‘you may go now’ and ‘Ne Si Na Pe’ means ‘he may go there’ in that code language.
II. ‘Ki Se Pe Bo’ means ‘come there and See’ and ‘Se Ni Bo Ki’ means ‘come here and see’ in that code language.
12. What is Keshav’s rank in a class of 50 ?
I. Amit, ranking 18th in the class from the top, is 7 ranks below Vivek, who is 5 Ranks above Keshav.
II. Saurav, the 10th from the bottom, is 20 ranks below Suresh, who is 5 ranks below Keshav.
13. How is Ram related to Nitin ?
I. Revati, Nitin’s Mother, is cousin of Sukesh, the uncle of Ram.
II. Pravin, Ram’s father-in-law, is the grandfather of Sachin, the nephew of Nitin.
14. Who among M, N, O, P and Q is the youngest ?
I. N, the 2nd youngest, is younger than Q, O and M.
II. O, the 2nd oldest, is older than N.
15. Who among P,Q, R, S and T is the shortest ?
I. R, though not the shortest, is shorter than only Q.
II. S, though not as tall as P, is not the shortest.
Directions (Q. 16-20) : In each of the questions below are given three statements followed by four conclusions numbered I, II, III and IV. You have to take the given statements to be true even if they seem to be at variance with commonly known facts. Read all the conclusions and then decide which of the given conclusions logically follows from the given statements disregarding commonly known facts.
16. Statements : Some desks are mirrors. Some mirrors are combs. Some combs are pins.
Conclusions :
I. Some pins are desks.
II. Some combs are desks.
III. Some pins are mirrors.
IV. Some pins are either desks or mirrors.
(a) None follows
(b) Only II follows
(c) Only I follows
(d) Only IV follows
(e) Only III follows
17. Statements : All blades are hammers. All hammers are rods. All rods are buckets.
Conclusions :
I. Some buckets are hammers.
II. Some rods are blades.
III. All hammers are buckets.
IV. All blades are rods.
(a) Only I and II follow
(b) Only II and III follow
(c) Only I, II and III follow
(d) Only II, III and IV follow
(e) All follow
18. Statements : All trees are chairs. No chair is flower. Some flowers are bangles.
Conclusions :
I. No tree is bangle.
II. No chair is bangle.
III. Some flowers are trees.
IV. Some bangles are trees.
(a) None follows
(b) Only either I or IV follows
(c) Only either II or III follows
(d) Only I and II follow
(e) Only III and IV follow
19. Statements : All rocks are balls. Some balls are rings. All rings are stones.
Conclusions :
I. Some stones are rocks.
II. Some rings are rocks.
III. Some balls are rocks.
IV. No stone is rocks.
(a) Only I and III follow
(b) Only III and IV follows
(c) Only either I or IV and III follow
(d) Only either I or IV follows
(e) None of these
20. Statements : All books are papers. All pencils are papers. All tables are papers.
Conclusions :
I. Some books are pencils.
II. Some pencils are tables.
III. Some tables are books.
IV. Some papers are tables.
(a) Only I follows (b) Only III follows
(c) Only III follows (d) Only IV follows
(e) None of these
Directions (Q. 21-25) : Study the following arrangement carefully and answer the questions given below :
M4PA3%R#EJ2$DF1UHB@9TWI8KN6©V7ZQ
21. If all the symbols in the above arrangement are dropped, which of the following will be the seventeenth from the left end ?
(a) 1
(b) F
(c) 9
(d) B
(e) None of these
22. Which of the following is the eighth to the right of the twentieth from the right end of the above arrangement ?
(a) T
(b) %
(c) 2
(d) 6
(e) None of these
23. How many such consonants are there in the above arrangement each of which is immediately preceded by a number but not immediately followed by another consonant ?
(a) None
(b) One
(c) Two
(d) Three
(e) More than three
24. Four of the following five are alike in a certain way based on their positions in the above arrangement and so form a group. Which is the one that does not belong to that group ?
(a) R#J
(b) 9BW
(c) PM3
(d) 6VK
(e) 2DU
25. How many such numbers are there in the above arrangement each of which is immediately preceded by a consonant and immediately followed by a symbol ?
(a) None
(b) One
(c) Two
(d) Three
(e) More than three
Directions (Q. 26-30) : In the following questions, the symbols @,©,%, $ and ¬ are used with the following meaning as illustrated below :
‘P@Q’ means ‘P is not smaller than Q’.
‘P *Q’ means ‘P is neither greater than nor equal to Q’.
‘P©Q’ means ‘P is neither greater than nor smaller than Q’.
‘P$Q’ means ‘P is not greater than Q’.
‘P%Q’ means ‘P is neither smaller than nor equal to Q’.
Now in each of the following questions assuming the given statements to be true, find which of the three conclusions I, II and III given below them is/are definitely true and give your answer accordingly.
26. Statements : R @ V, V $J, J* K
Conclusions :
I. K % R
II. J @ R
III. K % V
(a) Only I is true
(b) Only II is true
(c) Only I and II are true
(d) Only III is true
(e) None of these
27. Statements : D % H, H @ V, V $ W
Conclusion :
I. H % W
II. D % V
III. D % W
(a) Only I is true
(b) Only II is true
(c) Only III is true
(d) All are true
(e) None of these
28. Statements : M $ T, T * J, J © N
Conclusions :
I. N % M
II. J % M
III. M $ N
(a) Only I is true
(b) Only II is true
(c) Only I and II are true
(d) All are true
(e) None of these
29. Statements : N $ R, R © D, D*K
Conclusions :
I. K % R
II. D % R
III. D @ R
(a) Only either II or III and I are true
(b) Only either II or III is true
(c) Only III is true
(d) All are true
(e) None of these
30. Statements : F © K, K % M, M ©T
Conclusion :
I. T*K II. F % M
III. T*F
(a) Only I is true
(b) Only II is true
(c) Only I and II are true
(d) Only II and III are true
(e) All are true
Directions ( Q. 31-35) : In each question below is given a group of letters followed by four combinations of digits/ Symbols numbered 1,2,3 and 4 You have to find out which of the combinations correctly represents the group of letters based on the digit/symbol code of each letter and the conditions those follow and mark your answer accordingly. If none of the combinations correctly represents the group of letters mark answer (e) i.e. none of these
Letter : M K A D E T R J I W U B F H Q
Digit/symbol Code :
7 % $ 6 5 8 1 9 2 @ # © * 3 4
Conditions :
(i) If the first letter is a consonant and the last letter is a vowel both are to be coded as the code for the vowel.
(ii) If the first letter is a vowel and the last letter is a consonant, the codes for the first and the last letters are to be interchanged.
(iii) If the third letter is a vowel it is to be coded as ‘S’.
31. WHIMTD
(a) @3d786
(b) @32786
(c) 63273@
(d) @3278@
(d) None of these
32. WEMKUD
(a) @5d %#6
(b) @d7%#6
(c) 657%#@
(d) @57%#@
(e) None of these
34. KMDFHE
(a) %76*35
(b) 576*35
(c) 576*3%
(d) %76*3%
(e) None of these
35. QTRUJE
(a) 48d#95
(b) 481#95
(c) 581#94
(d) 581#95
(e) None of these
Directions (Q. 36-40) : Study the following information carefully and answer the questions.
P, Q, R, S, T, V, W and Z are sitting around a circle facing at the centre. R is third to the right of Z, who is second to the right of P.S is not an immediate neighbour of Z and R.T is third to the left of S. Q is third to the right of W, who is not an immediate neighbour of S.
36. Which of the pairs of persons are the immediate neighbours of P ?
(a) VQ
(b) VW
(c) VS
(d) SR
(e) None of these
37. What is Q’s position with respect to Z ?
(a) Fourth to the right
(b) Fourth to the left
(c) Third to the right
(a) Only (A)
(b) Only (B)
(c) Only (C)
(d) Either (A) or (B)
(e) None of these
38. Who is second to the right of T ?
(a) Z
(b) Q
(c) W
(d) Data inadequate
(e) None of these
39. In which of the following pairs is the second person sitting on the immediate left of the first person ?
(a) RT
(b) TW
(c) QR
(d) Data inadequate
(e) None of these
Directions (Q. 41-45): In Making decisions about important questions, it is desirable to be able to distinguish between “strong” arguments and “weak” arguments. “Strong” arguments must be both important and directly related to the questions. “Weak” arguments may not be directly related to the question and may be of minor importance or may be related to the trivial aspects of the questions.
Each question below is followed by two arguments numbered I and II. You have to decide which of the arguments is a “Strong” arguments and which is a “weak” argument.
41. Should smoking cigarettes and drinking alcohol by the actors be completely banned in the movies in India ?
Arguments :
I. Yes, this will significantly reduce the trend of smoking cigarettes and drinking alcohol among the youth in India.
II. No, there should be no such ban on the creative pursuits of the filmmaker.
III. No, the films portray the society and hence such scenes should be an integral part of the movie if the story line demands so.
(a) None is strong
(b) Only I and II are strong
(c) Only II and III are strong
(d) Only I and III are strong
(e) All are strong
42. Should sale of vital human organs be made legal in India ?
Arguments :
I No, it goes against our culture.
II No, this will lead to unhealthy practices.
III Yes, this will bring an end to the illegal trading of human organs.
(a) None is strong
(b) Only I and II are strong
(c) Only III is strong
(d) Only II and III are strong
(e) All are strong
43. Should the conscription of citizens for defence services be made compulsory in India ?
Arguments :
I. Yes, this is the only way to tackle the serious shortage of manpower in defence services.
II. No, instead the compensation package be made comparable to other job sectors to attract people to join defence services.
III. Yes, many other countries have made this compulsory.
(a) Only I is strong
(b) Only II is strong
(c) Only I and II are strong
(d) Only either I or II is strong
(e) None of these
44. Should the salary and perquisites of public sector undertaking employees be made equivalent to those in the private sector ?
Arguments :
I Yes, this will help the public sector under takings to attract and retain competent workforce.
II No, public sector undertakings cannot afford to pay salaries to the level of private sector.
III Yes, otherwise the public sector undertakings will not be able to compete with the private sector organisations.
(a) None is strong
(b) Only III is strong
(c) Only I is strong
(d) Only II is strong
(e) Only I and III are strong
45. Should there be a complete ban on registration of new cars for a few months in the big cities in India.
Arguments :
I. Yes, this will significantly reduce the number of cars on the already overcrowded roads of the big cities in India.
II Yes, the existing car owners will be very happy as they will face less traffic snarls in peak hours.
III No, this is highly discriminatory against those who decide to buy cars now and hence should not be enforced.
(a) Only I strong
(b) Only and III are strong
(c) Only III is strong
(d) All are strong
(e) None of these
Directions (Q. 46-50) : Study the following information carefully and answer the given questions:
A word and number arrangement machine when given an input line of words and numbers rearranges them following a particular rule in each step. The following is an illustration of input and rearrangement.
Input : Word 32 73 verb 26 new desk 19
Step I : 73 word 32 verb 26 new desk 19
Step II : 73 desk word 32 verb 26 new desk 19
Step III : 73 desk 32 word verb 26 new 19
Step IV : 73 desk 32 new word verb 2619
Step V : 73 desk 32 new 26 word verb 19
Step VI : 73 desk 32 new 26 verb word 19
Step VII : 73 desk 32 new 26 verb 19 word and Step VII is the last step of the
above input. As per the rules followed in the above
steps, find out in each of the following questions
the appropriate step for the given input.
46. Step II of an input is : 51 brown 22 36 49 cloud sky red. How many more steps will be required to complete the rearrangement ?
(a) Three
(b) Four
(c) Five
(d) Six
(e) None of these
47. Step III of an input is : 58 dine 43 18 tower silver mat 24,
(a) 58 dine 43 mat 24 silver 18 tower
(b) 58 dine 43 mat 24 18 tower silver
(c) 58 dine 43 mat 18 tower silver 24
(d) there will be no such step.
(e) None of these
48. Input : 85 23 96 case over for 42 win.
How many steps will be required to complete the re-arrangement ?
(a) Four
(b) Seven
(c) Five
(d) Six
(e) None of these
49. Step IV of an input is : 63 car 51 eyes 25 36 store lane. Which of the following is definitely the input ?
(a) eyes car 25 63 36 51 store lane
(b) eyes 25 car 63 51 36 store lane
(c) eyes car 51 63 36 Store lane
(d) Cannot be determined
(e) None of these
50. Input : field eyes 94 32 house rent 49 27 Which of the following steps will be the last but one ?
(a) VI
(b) V
(c) VII
(d) VIII
(e) None of these
Directions (Q. 51-55) : In each question below is given a statement followed by two courses of action numbered I and II. A course of action is a step or administrative decision to be taken for improvement, follow up or further action in regard to the problem policy, etc. On the basis of the information given in the statement, you have to assume everything in the statement to be true, then decide which of the suggested courses of action logically follow (s) for pursuing.
Give answer (a) : If only I follows.
Give answer (b) : If only II follows.
Give answer (c) : If either I or II follows.
Give answer (d) : If neither I nor II follows.
Give answer (e) : If both I and II follow.
51. Statement : There has been a spurt of robbery and house breaking incidents in one locality during the past fortnight.
Courses of action :
I The local police station personnel should start patrolling the locality at regular intervals.
II The residents in the locality should be asked by the police authority not to leave their houses during the night.
52. Statement : Money has become more important than the game itself in the case of India cricket.
Courses of action :
I Govt. should put a cap on the earnings from different sources of the Indian cricket board.
II Govt. should cap on the earnings from different sources of Indian cricket players.
53. Statement : Very large numbers of people from northern part of the city are suffering from water-borne diseases.
Courses of action :
I The municipal authority should advise people living in the area not to use water supplied through pipeline for drinking purpose.
II The local hospitals should be put on high alert to tackle the emerging crisis situation.
54. Statement : The quality of foodgrains being distributed in some parts of the country through Public Distribution System is very poor and not fit for human consumption.
Courses of action :
I The entire stock of foodgrains should immediately be withdrawn from the distribution system.
II People should be advised to return the food grains purchased from the system and take their money back.
55. Statement : A large number of people gathered on the high way, blocking the traffic movement to protest the killing of five locals by a speeding vehicle.
Courses of action :
I The police should fire teargas shells to disperse the crowd.
II The police authority should calm down the sentiment of the crowd, assuring action against the culprit and deploy police personnel at the spot.
Directions (Q. 56-60) : In each of the following questions, two rows of numbers are given. The resultant number in each row is to be worked out separately based on the following rules and the question below the rows of numbers are to be answered. The operation of numbers progresses from left to right. Rules :
(i) If and odd number is followed by another composite odd number, they are to be multiplied.
(ii) If an even number is followed by an odd number, they are to be added.
(iii) If an even number is followed by a number which is a perfect square, the even number is to be subtracted from the perfect square.
(iv) If an odd number is followed by a prime odd number, the first number is to be divided by the second number,
(v) If an odd number is followed by an even number, the second one is to be subtracted from the first one.
56. 58 17 5 85 5 nIf ‘n’ is the resultant of the first row what is the resultant of the second raw?
(a) 225
(b) 32
(c) 49
(d) 4
(e) None of these
57. 24 64 15 m 11 15If m is the resultant of the first row, what is the resultant of the second row ?
(a) 165
(b) 75
(c) 20
(d) 3
(e) None of these
58. 7 21 3 d 7 33
If d is the resultant of the first row, what will be the resultant of the second row?
(a) 40
(b) 138
(c) 231
(d) 80
(e) None of these
59. 73 34 13 32 P 15
If P is the resultant of the first row, what is the resultant of the second row?
(a) 713
(b) 50
(c) 20
(d) 525
(e) None of these
60. 14 5 9 24 w 88
If w is the resultant of the first row, what is the resultant of the second row?
(a) 171
(b) 283
(c) 195
(d) 165
(e) None of these
Directions (Q. 61-65) : Below is given a passage followed by several possible inferences which can be drawn from the facts stated in the passage. You have to examine each in inference separately in the context of the passage and decide upon its degree of truth of falsity.
Mark answer (a) : If the inference is “definitely true”, i.e. it properly follows from the statement of facts given.
Mark answer (b) : If the inference is “probably true’ though not definitely true” in the light of the facts given.
Mark answer (c) : If the “data are inadequate”, i.e. from the facts given you cannot say whether the inference is likely to be true or false.
Mark answer (d) : If the inference is “probably false” though not “definitely false” in the light of the facts given.
Mark answer (e) : If the inference is definitely false”, i.e. it cannot possibly be drawn from the facts given or it contradicts the given facts.
In an era of globalisation we need to find appropriate tools to confront the challenges facing agriculture. Commodity futures market can play a major role in addressing some of these challenges. In order to improve agricultural productivity, we need to encourage private investment including that from individual farmers, and reasonable returns for agri produce is a prerequisite for this. The price appreciation in agri commodities has failed to match the increase in price of inputs or the price rise of other commodities, indicating deterioration terms of trade for agriculture. Our spot markets are fragmented and, being dominated by a large chain of intermediaries, can hardly ensure a fair return for the farmers. Spot transactions, being mostly offline, lack audit trail. Different prices for the same commodity in different parts of the country give rise to arbitrage opportunities for traders. Further, driven by the need for immediate cash, most farmers engage in distress sale after harvest when supply exceeds demand and price is at its lowest.
61. Private are largely benefited due to distress sale of agriculture produces.
62. Traders are largely benefited due to distress sale of agriculture produces.
63. Prices of agricultural produces are comparable throughout the country.
64. The prices of agricultural produce do not generate expected return at present.
65. Traders are at a disadvantage for lack of organised trade practices of agricultural produces.
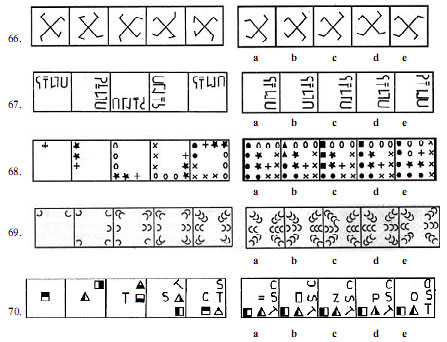
Directions (Q. 66-70) : In each of the questions given below which one of the five answer figures on the right should come after the problem figures on the left, if the sequence were continued?
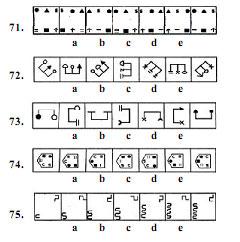
Directions (71-75) : In each of the following questions a series begins with an unnumbered figure on the extreme left. One and only one of the five numbered figures in the series does not fit into the series. The two unnumbered figures, one each on the extreme left and the extreme right, fit into the series. You have to take as many aspects into account as possible of the figures in the series and find out the one and only one of the five numbered figures which does not fit into the series. The number of that figure is the answer.
No comments:
Post a Comment